LactoSpore®
- A versatile probiotic
- Lactic Acid Bacillus
- Originally known in literature as Lactobacillus sporogenes
- also known as Bacillus coagulans
- L. sporogenes was first isolated and described in 1933 by L.M. Horowitz Wlassowa & N.W. Nowotelnow
- Documented clinical effectiveness
Characteristic Features
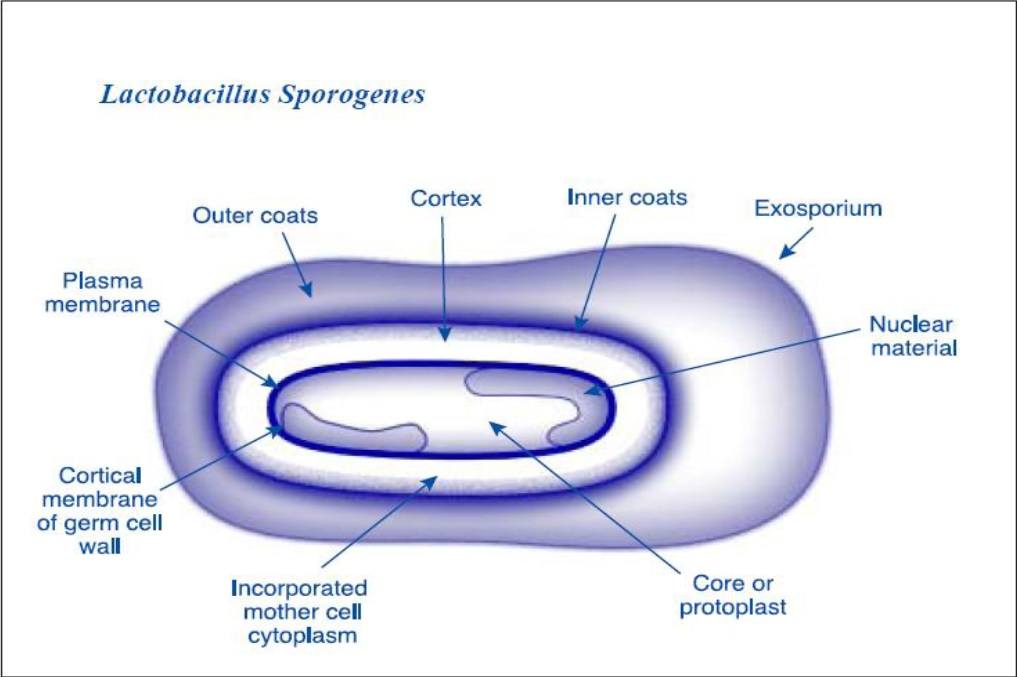
- Gram positive, Indole negative, rod shaped bacteria with terminal spores
- Produces L(+) Lactic Acid only
- Naturally microencapsulated for stability
- Proliferates within the GI tract
- Extremely fastidious organisms
- Grow optimally at 30°C to 37°C & optimum pH in the range 5.5 to 6.2
- Microaerophilic
- The acidic environment created by production of L(+) Lactic Acid & other antimicrobial compounds prevents the growth of disease causing microbes like Clostridia, which are responsible for production of undesirable gases
- Long & slender cells (0.3 to 0.8 microns)
- Colonies are usually 2.5 mm in diameter, convex, smooth, glistening and do not produce any pigment
Lactobacillus sporogenes
Temperature Stability
- Due to spore forming nature, LactoSpore® survives manufacturing, shipping and storage with no loss of viable count
- Does not require refrigeration conditions
- Cardiovascular support
- Room temperature stable
Lactic Acid Production
- LactoSpore® produces only L (+) Lactic acid, which is completely and efficiently metabolized to glycogen
- Whereas other probiotics may produce D (-) Lactic acid, which is metabolized slowly and in excess, can cause metabolic acidosis and may even be toxic to the brain
Gastrointestinal Health
Indicated for improvement of symptoms due to abnormalities in intestinal flora. A total of 567 cases in 19 institutions in Japan were evaluated.1
| Condition | % cases showing improvement |
Number of patients showing improvement |
|---|---|---|
| Diarrhea due to acute or chronic gastroenteritis |
93.7 | 118/126 |
| Maldigestion accompanied with diarrhea |
85.9 | 79/92 |
| Infantile diarrhea | 87.9 | 58/66 |
| Constipation | 65.4 | 17/26 |
1 - Abstracts of papers on the clinical study of Lacbon (Sporlac) compiled by the Sankyo Co. Ltd. Japan
Gastrointestinal Health: Studies in India
Study 1: Cases of neonatal diarrhea responded well to L. sporogenes (SPORLAC) therapy. 60 diarrheal cases of which three also suffered from constipation and three from jaundice were studied.
Dose administered: 15 million spores per day
Recovery period: 15 million spores per day
Recovery period: 1.8 days
Results summary for diarrheal symptoms:
| Condition | Cases Treated | Cases Cured | Success Rate |
|---|---|---|---|
| Diarrhea | 60 | 49 | 81.7% |
| Constipation | 3 | 3 | 100% |
| Jaundice | 3 | 3 | 100% |
Dhongade, R.K., Anjaneyulu, R. (1977). Abstract from Maharashtra Medical Journal Vol.XXIII No.1, Feb: 473-474
Study 2: 112 newborn infants in rural India were randomized to receive a daily oral dose of 100 million L. sporogenes or a placebo for one year.
Morbidity was monitored each week for 12 months.
| Effect of L. Sporogenes feeding on rotavirus diarrhea | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| L. Sporogenes | Placebo | p | |
| Number of Infants | 55 | 57 | |
| Number of Infants with Rotovirus Diarrhea |
44 | 50 | NS |
| Number of episodes |
3.4 (1.0) | 8.6 (1.7) | <0.02 |
| Duration of each episode (days) |
3.6 (1.0) | 6.8 (1.1) | <0.05 |
| Days ill / 12 months |
13 (3) | 35 (5) | <0.01 |
| Data are shown as mean (SD). NS: statistically not significant | |||
Chandra, R.K. Nutrition Research 22 (2002) 65–69
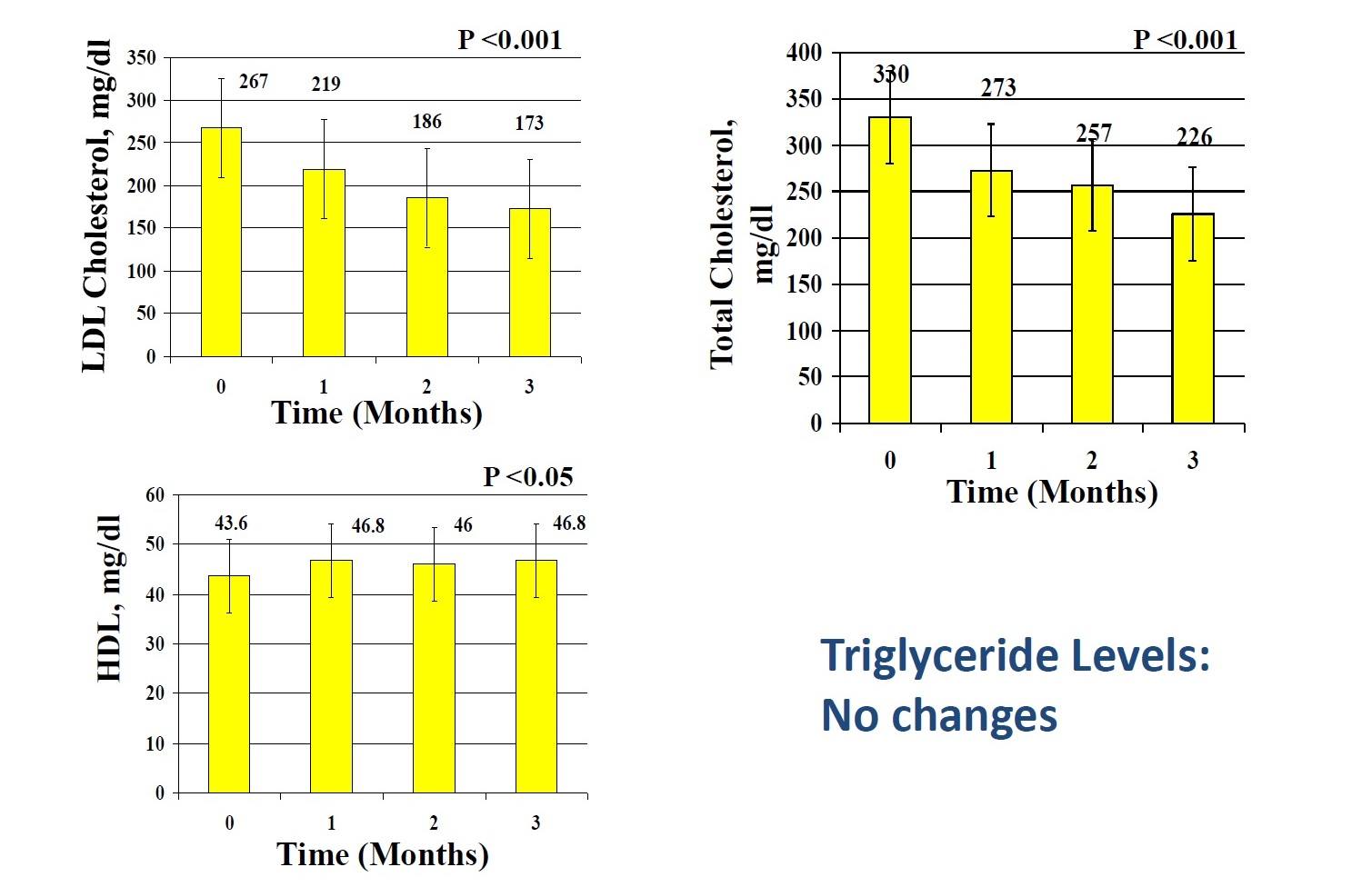
Other Clinical Studies: Healthy Serum Lipid Profiles
Short term hypolipidemic effects of oral L. sporogenes therapy
Dose: 360 million spores per day in tablet form
Subjects: 7 patients (15 men and 2 women in the 32-61 year age group) with type II hyperlipidemia in an open label fixed dose trial.
Duration: 12 weeks
Atherogenic Lipid Ratios were improved:
Total/HDL cholesterol ratio: Decreased by 27%
LDL/HDL ratio: Decreased by 33.4%
J.C. Mohan, R. Arora & M. Khalilullah, Indian Journal of Medical Research [B], 92:431-432 (1990)
Results of the Study
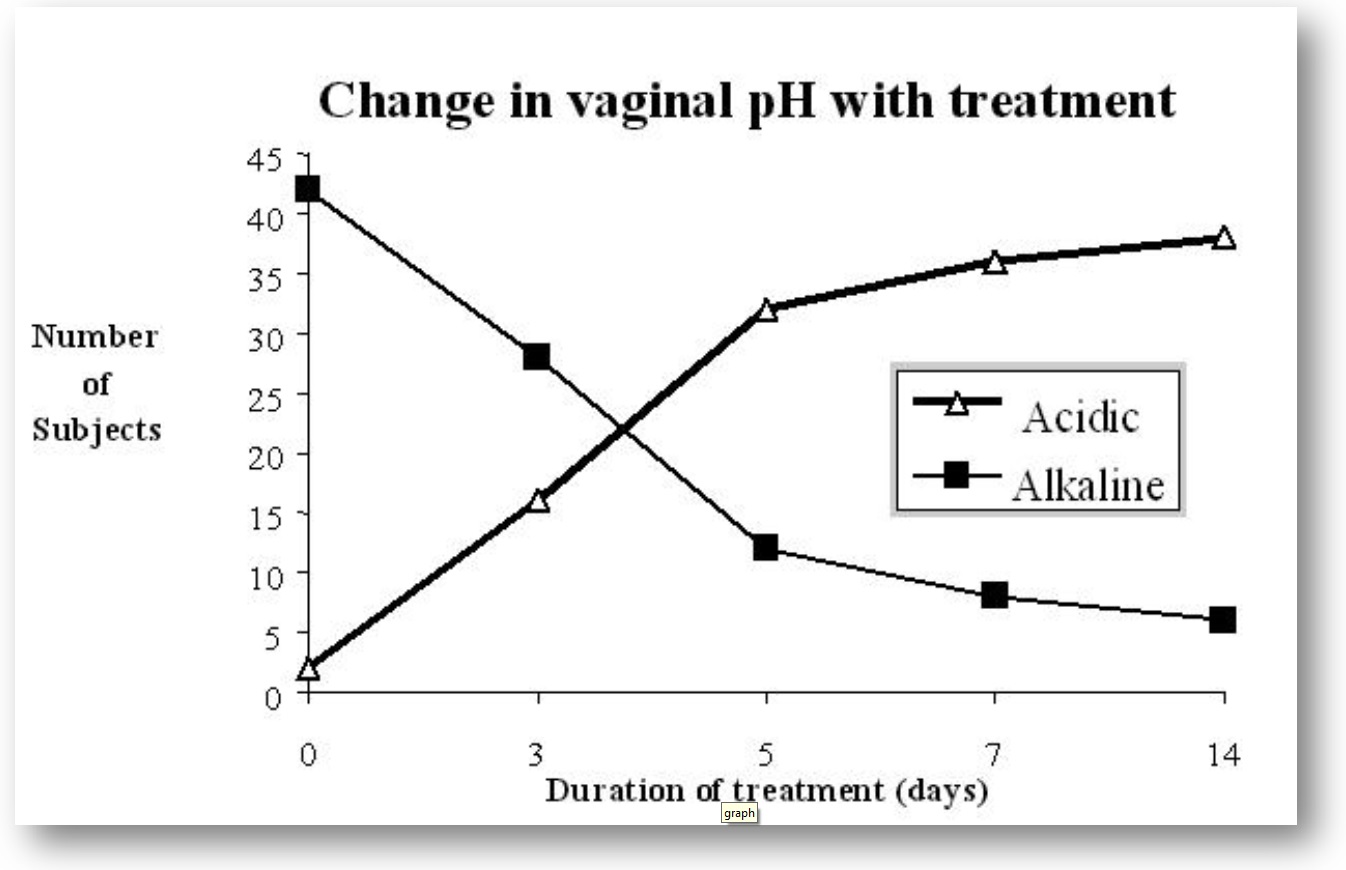
Clinical Study: Non-Specific Vaginitis
Study 2:44 patients with non-specific vaginitis [12 with leucorrhea after cervical surgery; 32 (26 of reproductive age and 6 postmenopausal, without previous therapy)]
Dose:2 vaginal tablets/day (150 million spores/tab.)
7-14 days
Results:
Complete relief: 91% cases
Partial relief: 9% cases
In a similar clinical trial using M.T.P. vaginal peccaries containing broxyquinoline and brobenzoxeldine where only 26.67% of cases studied were cured.
Conclusion:Lactobacillus sporogenes is effective in non-specific vaginitis by raising the vaginal acidity, and thereby checking the growth of pathogenic organisms.
Non-Specific Vaginitis
Sankholkar, P.C and Sali, M.S. Clinical study report from B.J. Medical College, Pune, India
Aphthous stomatitis and glossitis
- Recurrent oral lesions respond well to Lactobacillus sporogenes therapy
120 million spores supplied in three divided doses (in the form of SPORLAC, a tabletted preparation) for three days was found to be effective in human volunteers.
Mathur, S.N. et al. (1970). UP State Dental Journal 11:7-12
Other Health Benefits in Infants
Condition: Allergic Skin Diseases
- No. of subjects: 5
- Treatment: 200-450 million spores / day in divided doses for 4-12 days
- Effectiveness rate: 80.0%
Conclusion: Obvious eruptions of strophulus and eczema decreased from the third day (topical therapy employed concomitantly)
Condition: Miscellaneous Symptoms
- No. of subjects: 10
- Treatment: 20-50 million spores / day in divided doses for 4-20 days
- Effectiveness rate: 80.0%
Conclusion: Response seen in anorexia of nervous type and malnutrition in infants
Abstracts of papers on the clinical study of Lacbon (Sporlac) compiled by the Sankyo Co. Ltd. Japan
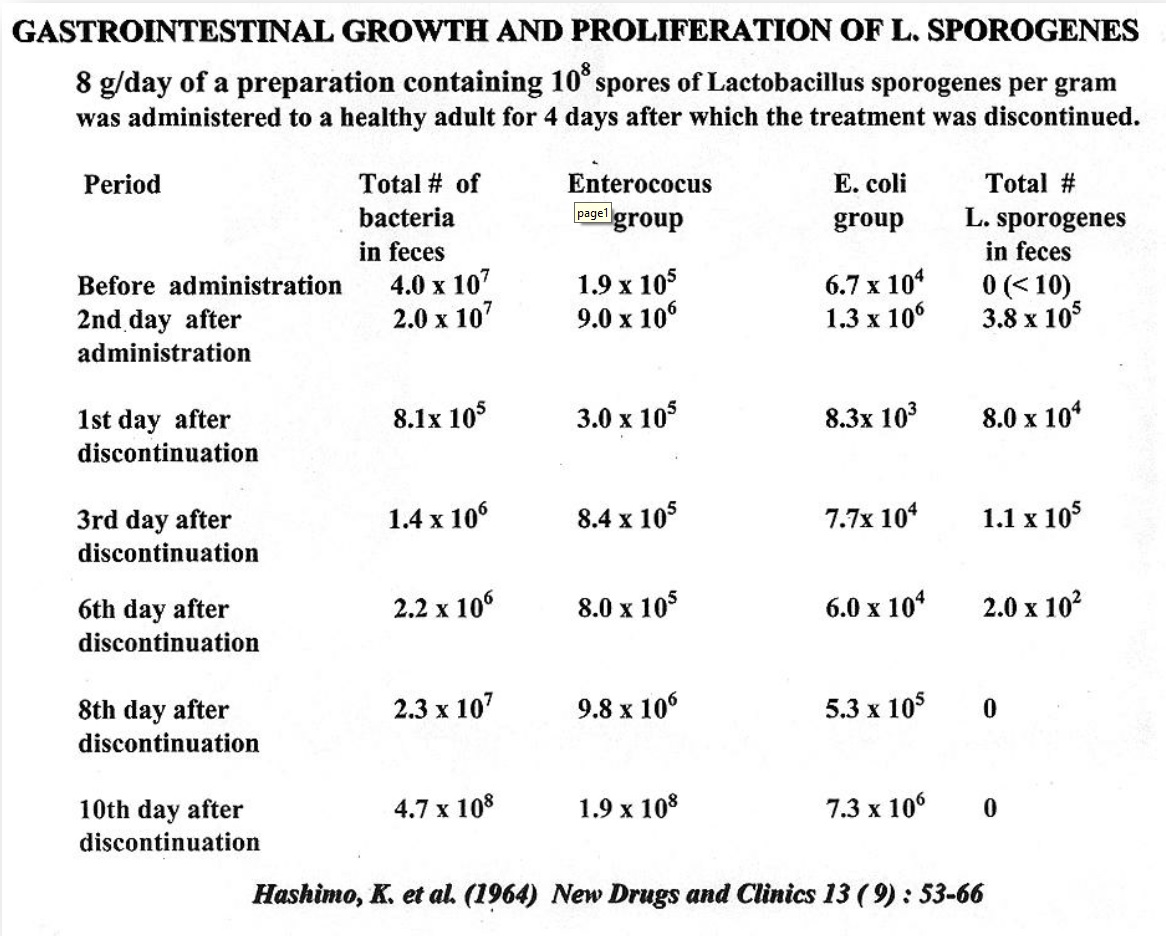
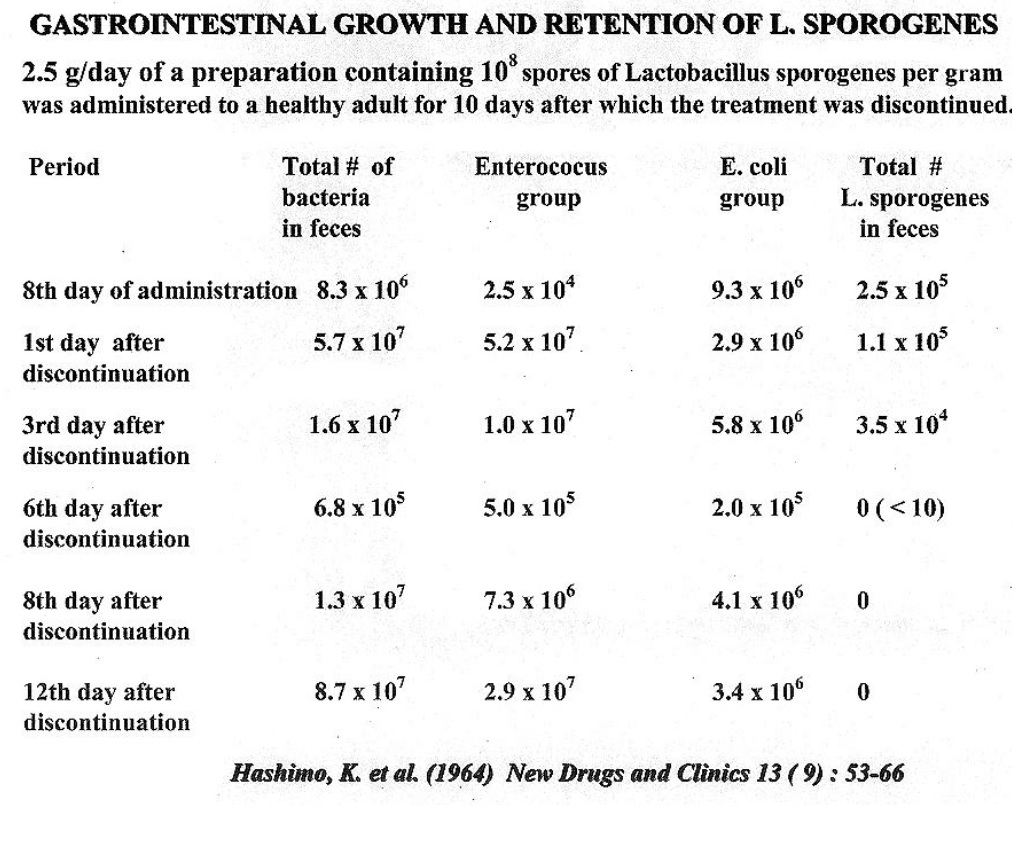
Advantages of LactoSpore®
- Produces L(+) Lactic acid only
- Produces Bacteriocin
- Room temperature stable
- Clinical studies have revealed that it can be successfully implanted in the intestine